A settlement layer plays a fundamental role within blockchains by ensuring the final and irreversible validation of transactions. How does this technology layer actually work? How does it differ from other layers of a blockchain architecture?
What is a settlement layer?
In a blockchain, several steps follow one another before a transaction is considered final and added to the history.
When a transaction is requested by a user, it all starts with the execution layer, which processes the transaction by executing smart contracts. Then, this transaction, once verified and deemed valid, is transmitted to the settlement layer.
This layer acts as the final arbiter, ensuring that the transaction state complies with blockchain rules and that it will be immutably registered within a block.
The settlement layer is therefore responsible for finalizing transactions. This means thatonce a transaction is validated by this layer, it can no longer be modified or disputed. It becomes definitive.
Cryptoast Academy: Don’t waste this bull run, surround yourself with experts
Difference between modular blockchains and monolithic blockchains
THE blockchain traditional (or monolithic) such as Bitcoin consolidate all functions (execution, consensus, data management and settlement) into a single layer.
Each node in the network must therefore process all aspects of a transaction, which can lead to limitations in terms of scalability and efficiency.
On the other hand, modular blockchains take a different approach by separating these functions into distinct layers.
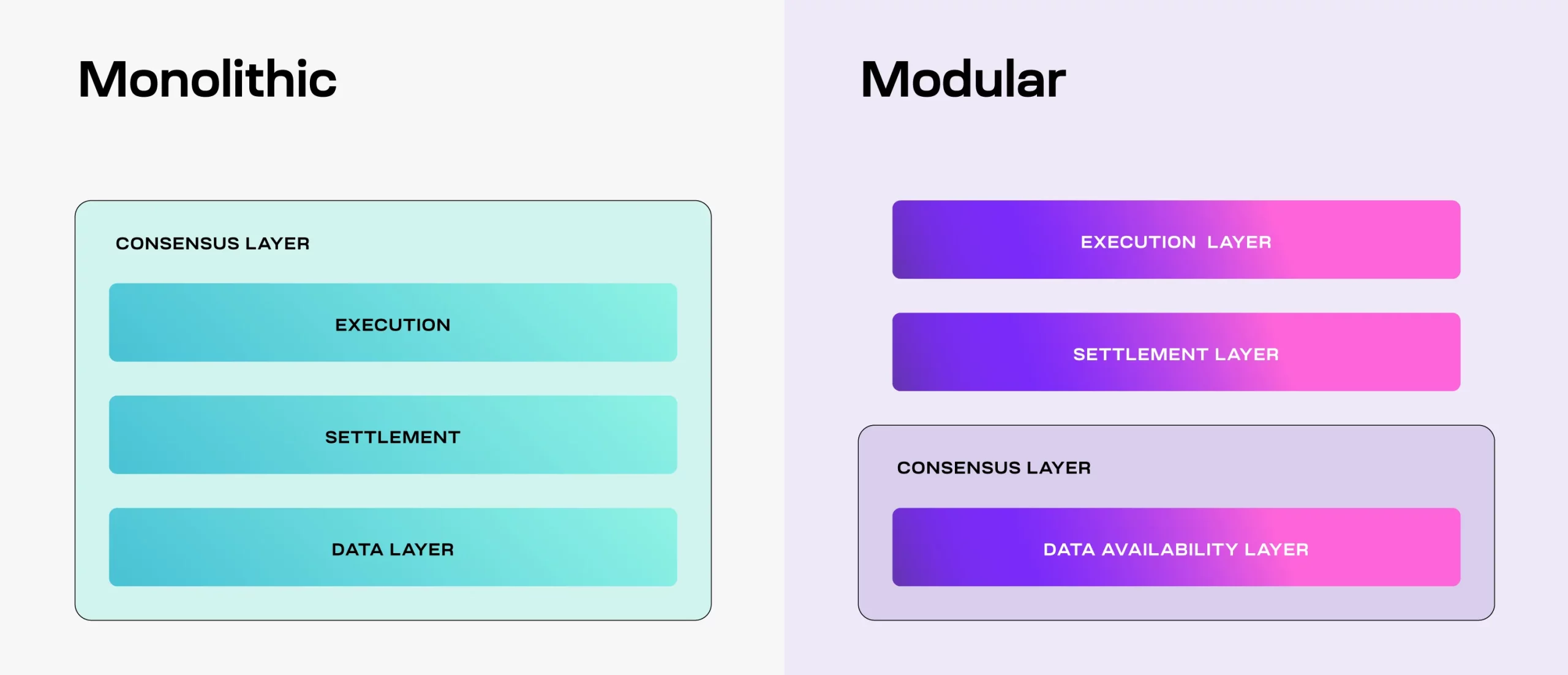
Layer architectures of monolithic and modular blockchains – Source: IntoTheBlock
This architecture allows optimization of the performance of each layer. For example, Celestia is a modular blockchain that distributes tasks between different layers, where the settlement layer focuses only on the final validation of transactions.
The role of the settlement layer in the blockchain
Finality of transactions and immutability
One of the main functions of the settlement layer is to guarantee the finality of transactions. In other words, once a transaction is validated and written to a block via this layer, it becomes immutable.
This means that it can no longer be canceled or modified, even in the event of a dispute or error.
This immutability is essential for the proper functioning of a blockchain, because it establishes trust between participants. Once a transaction is settled, it becomes irreversible, providing users with the certainty that the transactions are final.
For example, within layer 2 solutions such as optimistic rollup, transactions are processed off the main chain to increase scalability. However, these transactions still need to be validated by the settlement layer in order to be permanently listed on the main chain.
Verification of evidence and resolution of disputes
In addition to validating transactions, the settlement layer is responsible for verifying proofs.
For example, in the case of optimistic rollups, if an off-chain transaction is disputed, proof of fraud may be submitted to the settlement layer for verification. This mechanism ensures that only legitimate transactions are recorded in the immutable blockchain ledger.
The settlement layer also plays a key role in dispute resolution.
In multi-rollup environments, where multiple execution layers operate in parallel, this layer can serve as a bridge between different execution layers. It ensures that transactions from various sources are validated correctly and posted in order.
Cryptoast Academy: Don’t waste this bull run, surround yourself with experts
The importance of the settlement layer in blockchain security
The settlement layer is a pillar of blockchain security. By guaranteeing that each validated transaction is irreversible, This layer protects the integrity of the network against fraud attempts or errors.
In a modular blockchain, like Celestia, this layer is even more critical, because it must validate the results of several layers of execution.
Unlike other layers, which focus on transaction execution or data management, the settlement layer ensures that these operations are recorded permanently, thus establishing transparency and trust.
Interoperability and cost reduction
The settlement layer also promotes interoperability between different blockchains.
For example, in ecosystems like Polkadot or Cosmos, multiple blockchains interact to share information and process transactions. Thanks to validation provided by a common settlement layer, these blockchains can work together securely.
Another key benefit is cost reduction. By outsourcing certain execution functions of a blockchain to other layers, the settlement layer allows you to reduce processing costswhile maintaining a high level of security.
The example of the settlement layer in the evolution of Ethereum
Following its transition to Proof of Stake, the blockchain Ethereum gradually adopts a modular architecture to improve the scalability and efficiency of its network.
Unlike the monolithic version of Ethereum, where all functions were performed by a single entity, Ethereum 2.0 separates these responsibilities into several specialized layers.
In this new model, the settlement layer ensures that all transactions executed on layer 2 solutions are not only validatedbut also permanently registered on the main Ethereum chain.
Layer 2 solutions process a large number of transactions off the main chain to increase network capacity and reduce gas fees. However, to ensure network security and integrity, the results of these transactions must be validated and recorded immutably by the settlement layer.
Thus, even if the execution of transactions is outsourced, the finality and immutability of transactions are preserved by the main chain via the settlement layer, thus ensuring maximum security.
Cryptoast Academy: Don’t waste this bull run, surround yourself with experts
The #1 Crypto Newsletter 🍞
Receive a summary of crypto news every day by email 👌
What you need to know about affiliate links. This page may feature investment-related assets, products or services. Some links in this article may be affiliated. This means that if you buy a product or register on a site from this article, our partner pays us a commission. This allows us to continue to offer you original and useful content. There is no impact on you and you can even get a bonus using our links.
Investments in cryptocurrencies are risky. Cryptoast is not responsible for the quality of the products or services presented on this page and cannot be held responsible, directly or indirectly, for any damage or loss caused following the use of a good or service highlighted in this article. Investments related to crypto-assets are risky by nature, readers should do their own research before taking any action and only invest within the limits of their financial capabilities. This article does not constitute investment advice.
AMF recommendations. There is no guaranteed high return, a product with high return potential involves high risk. This risk-taking must be in line with your project, your investment horizon and your capacity to lose part of this savings. Do not invest if you are not prepared to lose all or part of your capital.
To go further, read our Financial Situation, Media Transparency and Legal Notices pages.










