Future Shanghai and Capella updates to the Ethereum blockchain will allow validators to withdraw ETH locked in the Beacon Chain or rewards obtained through staking. How will these withdrawals work? How long will you have to wait? All our answers in this article.
The arrival of Shanghai and Capella
The transition of the Ethereum (ETH) blockchain to Ethereum 2.0 started in December 2020 with the launch of the Beacoin Chain and Ether (ETH) staking functionality. Since then, in September 2022, the network hit a major milestone with The Merge.
This update made it possible to abandon Proof of Work (PoW) and to start block validation thanks to the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus of the Beacon Chain. Nevertheless, ETH rewards granted to validators since December 2020 are locked in a layer called “Consensus Layer (CL)” and are therefore inaccessible.
Since The Merge, stakers also receive transaction fee rewards when their validators offer blocks. These are sent to an address on a layer called “Execution Layer (EL)”and are also blocked.
However, these situations will soon change with Shanghai and Capella updates. The first one allow withdrawals of staked ETH on the Beacon Chain and the second will allow access locked rewards on the Execution Layer. These major updates are expected to occur in March 2023.
As of this writing, approximately 513,530 nodes are contributing to securing the Ethereum blockchain, with a locked amount of 16,432,807 ETH.
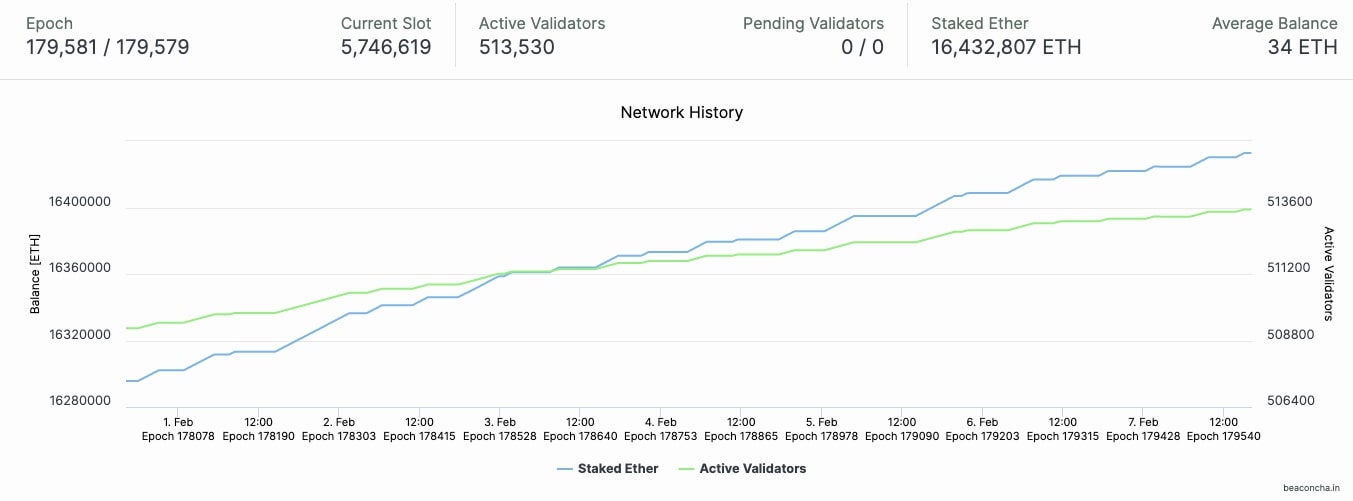
Beacon Chain status information

ETH crypto is available on Binance
-10% on your fees
How Ethereum withdrawals work
Two types of withdrawals
Following the Shanghai update, a first withdrawal functionality will be available for validators: “Unstaking”. Concretely, the validator’s current balance (32 ETH + rewards) is burned on the Consensus Layer and immediately minted on the so-called “Credential” address, directly on the Executive Layer.
The second withdrawal feature will be made possible after the Capella update: “Skimming”. The subtlety is that only the excess Ether on the validator balance (the amount above 32 ETH) is burned on the Consensus Layer and created on the Executive Layer.
In other words, it is important to hold this Credential address to recover the ETH locked in the Beacon Chain as well as rewards generated through staking. This address is defined and associated with the validation key generated during the deposit of the 32 ETH for the creation of the validator node.
How to unstake your ETH?
To operate this withdrawal, your Credential address will need to be in the format “0x01”. If this is not the case (therefore in a “0x00” format), here is the line of code to fill in and communicate to the Consensus Layer:
class BLSToExecutionChange(Container):
validator_index: ValidatorIndex
from_bls_pubkey: BLSPubkey
to_execution_address: ExecutionAddress
Finally, if a staker wants to unlock his position (i.e. the 32 ETH plus any rewards), it will then be possible to sign a voluntary exit message using the validation key obtained when creating the validator node and broadcasting it to the Consensus Layer for processing:
class BLSToExecutionChange(Container):
validator_index: ValidatorIndex
from_bls_pubkey: BLSPubkey
to_execution_address: ExecutionAddress
As soon as the validator’s output message is received, it joins the output queue. Note however that a validator in the output queue continues to offer and validate blocks. As a result, it therefore continues to earn rewards.

How long to wait?
The duration of the output queue for Ethereum validators is difficult to estimate. Indeed, it is dynamic and is based on several variables; notably :
- the total number of validators;
- the minimum termination limit (or “churn” in English), set to 4;
- and a termination limit quotient, set at 2^16 (i.e. 65,536).
These variables are then used to calculate the termination limit, i.e. the number of validators who can leave their positions at each Epoch. Note that an Epoch of the Ethereum blockchain is a period that lasts approximately 6.4 minutes and corresponds to 32 blocks.
So, the number of validators that can exit the queue every 6.4 minutes is calculated like this: the total number of validators divided by the quotient of the termination limit, rounded to the nearest whole number. Note that the minimum for this termination limit is 4:
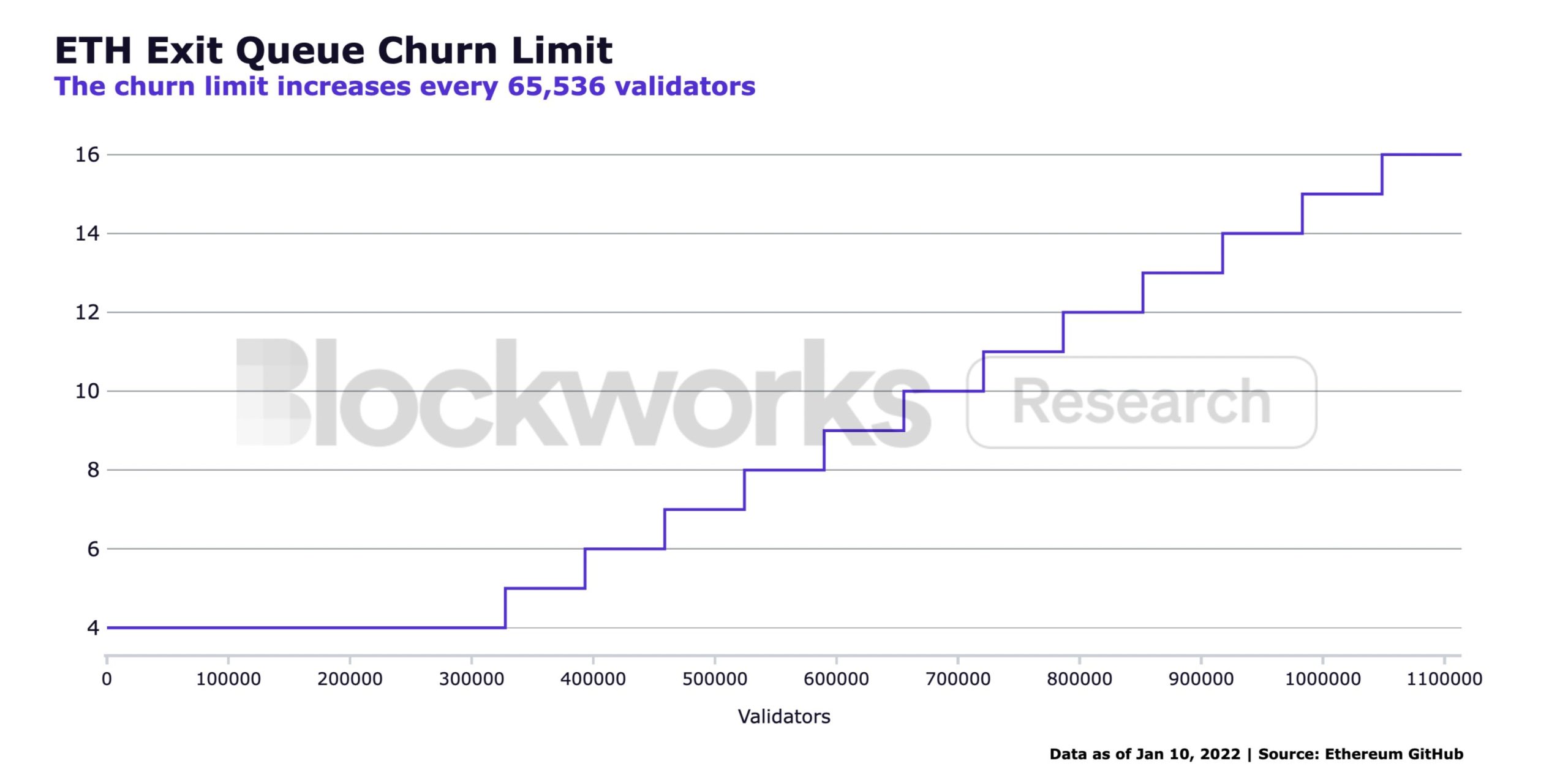
Evolution of the cancellation limit, i.e. the number of validators who can unstake at each Epoch
For information, once the validator is out of the queue, he will still have to wait during a withdrawal period. It is 256 Epochs (about 27 hours) or 8,192 Epochs (about 36 days) if the node has been slashed.
From these elements and these variables, it is therefore possible to estimate a duration for withdrawing ETH from staking.
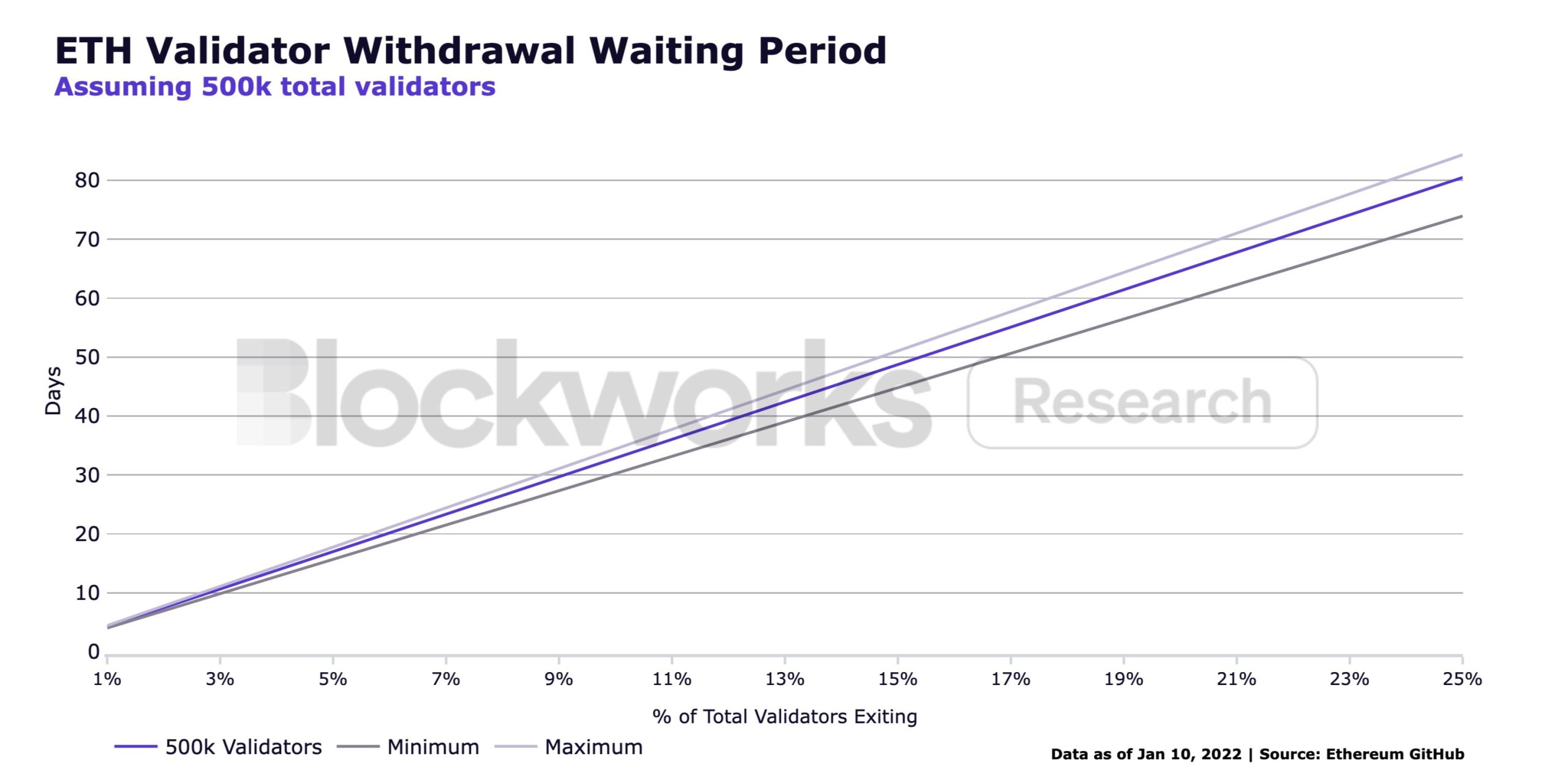
Estimated Queue Duration to Withdraw ETH from Validator
As shown in the figure above, it would take about 80 days if 25% of validators wanted to withdraw simultaneously and about 35 days if only 10% want to close their validator node. Concretely, everything will depend on the number of people wishing to keep or withdraw their Ethers from staking.
Of course, there is a possibility that validators decide to withdraw only their profits and keep their knot. In this precise case, these are partial withdrawals and they will be limited to 256 by Epoch. It means that 57,600 partial withdrawals can be processed in total every day.
So note that if the current 500,000 validators all wanted to partially opt out, it would take about 8.7 days.


1st Newsletter Free with the code TOASTNL

Source: Kiln, Blockworks Research
Newsletter
Receive a summary of crypto news every Monday by email
What you need to know about affiliate links. This page presents assets, products or services relating to investments. Some links in this article are affiliated. This means that if you buy a product or register on a site from this article, our partner pays us a commission. This allows us to continue to offer you original and useful content. There is no impact on you and you can even get a bonus by using our links.
Investments in cryptocurrencies are risky. Cryptoast is not responsible for the quality of the products or services presented on this page and could not be held responsible, directly or indirectly, for any damage or loss caused following the use of a good or service highlighted in this article. Investments related to crypto-assets are risky by nature, readers should do their own research before taking any action and only invest within the limits of their financial capabilities. This article does not constitute investment advice.
AMF recommendations. There is no guaranteed high return, a product with high return potential involves high risk. This risk-taking must be in line with your project, your investment horizon and your ability to lose part of this savings. Do not invest if you are not ready to lose all or part of your capital.
To go further, read our Financial Situation, Media Transparency and Legal Notices pages.











