A study published in the journal Cardiovascular Diabetology describes the relationship between estimated glucose disposal rate (eGDR) and retinopathy or kidney disease in young adults with type 1 diabetes.
The study finds that eGDR, a proxy marker of insulin resistance, can serve as a marker to identify at-risk type 1 diabetes patients.
 Study: Estimated glucose disposal rate is associated with retinopathy and kidney disease in young people with type 1 diabetes: a nationwide observational study. Image Credit: sciencepics / Shutterstock
Study: Estimated glucose disposal rate is associated with retinopathy and kidney disease in young people with type 1 diabetes: a nationwide observational study. Image Credit: sciencepics / Shutterstock
Background
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic health condition characterized by increased blood glucose levels due to a lack of pancreatic insulin production. The condition increases the risk of cardiovascular complications even in individuals with good glycemic control. Apart from hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, kidney disease, and hypertension increase the risk of cardiovascular complications in type 1 diabetes patients.
Insulin resistance is a major cause of hyperglycemia in diabetes patients. It occurs when cells in the body become unresponsive to insulin produced by pancreatic beta-cells. It is well-documented that in type 1 diabetes patients, insulin resistance is associated with macrovascular complications, including coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmias and sudden death, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral artery disease.
In the current study, scientists have determined the relationship between insulin resistance and microvascular complications (diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, and retinopathy) in young adults with type 1 diabetes.
Study design
The study analyzed the data obtained from the Swedish pediatric registry for diabetes (SweDiabKids) and the registry for adults (NDR). All individuals who have type 1 diabetes for a duration of less than 10 years were included in the analysis.
Based on the eGDR values, the individuals were divided into four categories (eGDR value: < 4, 4 to 5.99, 6 to 7.99, and ≥ 8 mg/kg/min). Within these categories, the incidence rate and the risk of retinopathy and kidney disease were determined.
The participants were followed from the date of registry (index date) until the detection of retinopathy or kidney disease or until the end of the study period (December 2017). The study was conducted between 1998 and 2017. In both retinopathy and kidney disease groups, the average age of participants at the index date was 21 years.
Various confounding factors were addressed in the analysis, including age, sex, eGDR estimates, lipid profile, glycemic index, body mass index (BMI), physical activity level, hypertension, and medications.
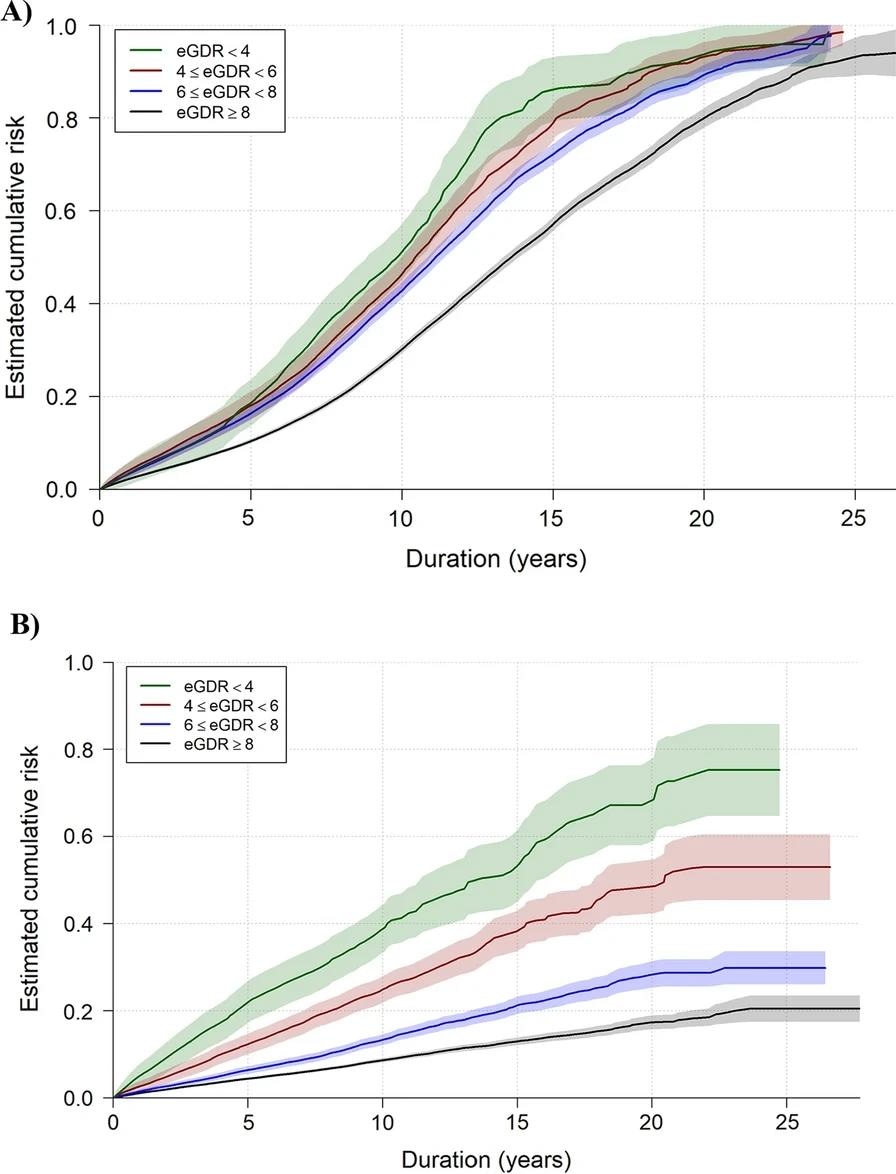
Estimated crude cumulative risk curves illustrated the accumulated estimated risk of retinopathy (A) and kidney disease (B) based on these observed time intervals in young people with type 1 diabetes (eGDR = estimated glucose disposal rate). The shaded are represents the 95% confidence interval of the estimated crude curves
Association between eGDR and retinopathy
The retinopathy group was followed up for an average of 4.8 years. The analysis conducted after adjustment for all confounding factors revealed that a lower eGDR estimate is associated with an increased risk of retinopathy.
Considering kidney disease as a confounding factor, no competing risk between retinopathy and kidney disease was observed.
Association between eGDR and kidney disease
The kidney disease group was followed up for an average of 5.4 years. The analysis conducted after adjustment for all confounding factors revealed that a lower eGDR estimate is associated with an increased risk of kidney disease. However, the same risk was not observed among the participants with the lowest eGDR (< 4 mg/kg/min).
Considering retinopathy as a confounding factor, no competing risk between retinopathy and kidney disease was observed.
In both retinopathy and kidney disease groups, the glycemic control estimate (HbA1c) was identified as the highest risk factor, followed by BMI and hypertension.
Study significance
The study indicates that a lower eGDR increases the risk of retinopathy and kidney disease in young adults with type 1 diabetes. A low eGDR is indicative of high insulin resistance.
As mentioned by the scientists, early detection of microvascular complications via eGDR estimation can reduce the risk of subsequent macrovascular complications and organ damage. In other words, eGDR can be used as a useful marker for identifying at-risk individuals with type 1 diabetes.
This is a large-scale nationwide, observational study with a long follow-up period. The scientists consider this as the major strength of the study. However, they mention that the eGDR formula used in the study has not been fully validated in the youth. Thus, they are unsure how accurately eGDR estimates reflect insulin resistance.
They highlight the need for future studies to more conclusively determine the impact of insulin resistance on micro- and macrovascular complications in type 1 diabetes patients.