Study reveals how mutual gazing and petting synchronize human and dog brains, while autism-related gene mutations in dogs reduce this connection.
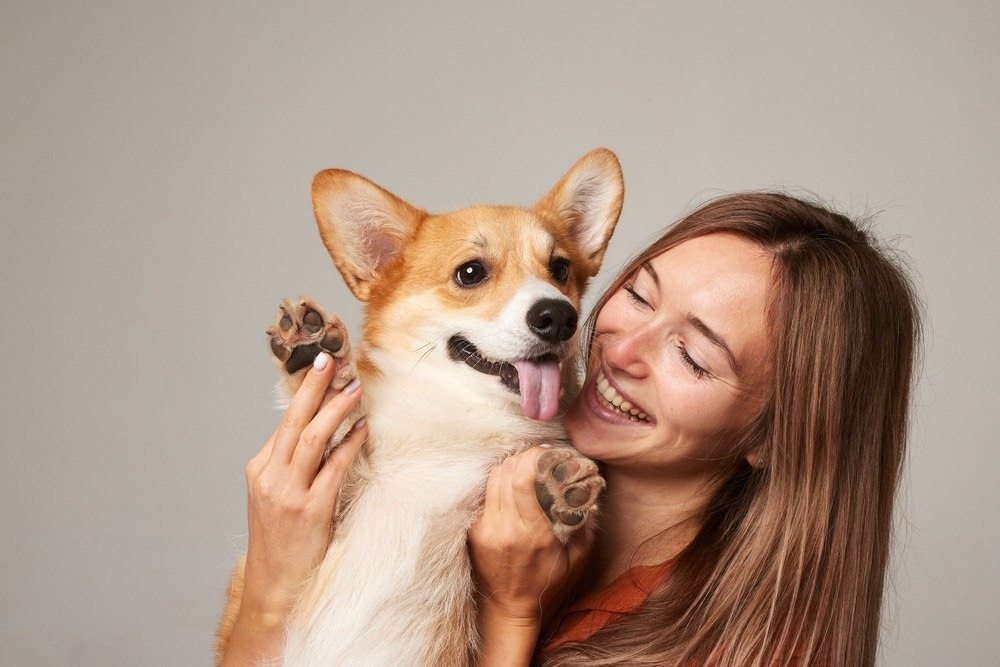

In a recent study published in Advanced Science, researchers studied cross-species interbrain connections between dogs and humans. They also investigated whether autism-related gene abnormalities in dogs impede social interaction between human-dog pairs.
Background
The human-dog connection has developed with time, with dogs tamed for their protective and hunting capacities. They have become valuable members of households, offering companionship and emotional support. Interspecies partnerships generate mutual benefit but seldom approach the extent of communication between humans and dogs. Dogs can read, comprehend, and react to various human emotions and linguistic signs via facial expressions, behaviors, and voice tones. However, the brain mechanisms underlying interspecies social communication remain unknown.
About the study
In the present study, researchers investigated the brain processes enabling human-dog communication. They explored the influence of autism-related gene alterations in dogs on social interactions between the two species.
Non-invasive wireless electroencephalograms (EEG) concurrently detected brain activity in beagles (research canines) and humans during social interactions. To validate the findings, researchers assessed interbrain correlations between different areas of the brain under three situations. The situations included no social interactions in separate spaces, with social interaction in one room and without social engagement in one room. Social interactions included petting and mutual gazing.
Researchers compared interbrain coupling during complete social interactions (mutual gaze + petting) to partial social interactions (mutual gaze or petting alone) to evaluate the synergistic effects of mutual gaze and petting on interbrain coupling. They also investigated brain activity associations between dogs and human participants from different trials and recorded the brain activities of the two species during social interactions for five days to evaluate the impact of social familiarity on interbrain neural coupling.
Subsequently, researchers conducted an additional five-day investigation to assess the durability or changes in interbrain interactions across prolonged periods. Linear regressions investigated the association between the duration of social interactions and interbrain activity. Generalized partial directed coherence (GPDC) algorithms assessed the directionality of interbrain activity coupling.
Researchers developed an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) model for dogs with SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domain 3 (Shank3) mutations using Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-associated protein 9 (Cas9) genome editing.
Behavioral studies such as the three-chamber test and human-dog interaction experiments revealed autism-like symptoms in the mutants. Over five days, researchers explored the interbrain neuronal connection between mutant canines and humans. Theta/beta wave ratios (TBR) indicated attention problems in the mutants during the social interactions between humans and dogs.
Researchers also explored the effects of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), a psychedelic, on brain function. They delivered a single dosage of 7.5 μg/kg bodyweight of LSD intramuscularly and observed its effects after 24 hours.
Results
Petting and mutual gazing resulted in interbrain synchronization in the parietal and frontal areas of the brain during human-dog interactions, respectively. These brain areas are involved in joint attention. The interbrain association in these brain areas of dogs and humans caused by mutual gazing or stroking alone was much lower than that during combined social interactions, including petting and mutual gazing.
Over five days, the synchronization intensity increased as the human-dog dyad became more familiar. Linear regression analyses revealed a strong positive association between social contact time, interbrain activity correlations, and GPDC values. After a week of social contacts, logistic growth curve regressions revealed that interbrain correlation in the frontal and parietal areas had plateaued.
Interbrain correlations between humans and dogs in various sessions were much lower than in the same interaction sessions. The findings demonstrate that reciprocal involvement between dogs and humans is vital for interbrain neural connections. During the human-dog social interactions, the human takes the lead, and the dog follows. The mutant canines displayed lower attention and eliminated interbrain connections. A single dosage of LSD corrected the problems.
Conclusions
The study found that interbrain neural synchronizations between family dogs and human beings are identical to those observed during human-human interactions. The frontoparietal network is essential for interbrain activity coordination and sensory information attention. Dogs with Shank3 mutations demonstrated poor brain circuitry and attention, comparable to those with ASD. A single dosage of LSD restored reduced interbrain connection and joint attention in the mutant dogs, indicating that LSD may improve social impairment in ASD patients.
The findings point to possible interbrain neural activity biological markers for autism spectrum disorder diagnosis and the development of designed non-hallucinogenic LSD analogs to address social deficiencies. Further research into brain coupling may improve the knowledge of the neurological mechanisms that underpin social interactions between regularly developing humans and those with mental illnesses like ASD.