Businesses face a myriad of information security risks that can be detrimental to their operations. These risks include, but are not limited to:
Phishing attacks. This type of cyber attack happens when hackers send fake links that look like they come from a trustworthy source. They do this to trick people into giving away private information like login details or financial data.
Malware infections. Malware is software designed to cause harm to a computer or network. Infections can range from annoying pop-ups to more serious problems such as data theft or system crashes.
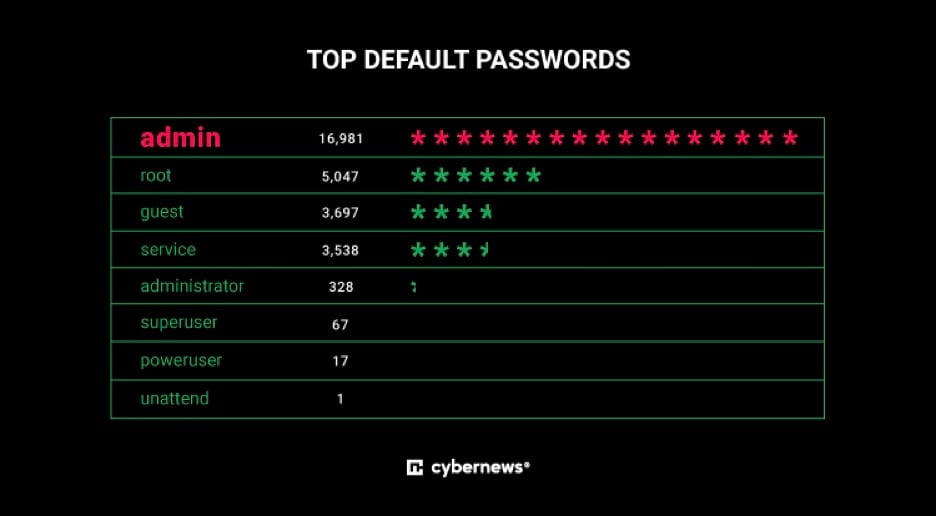
Weak passwords. Weak passwords can be easily guessed by hackers and can provide access to sensitive data. Hackers can discover passwords through various means, including brute force attacks, social engineering tactics, or by obtaining passwords from data breaches or leaks.
Unsecured Wi-Fi networks. Hackers have the ability to intercept data that is transmitted over unsecured Wi-Fi networks. This data can include sensitive information such as login credentials, financial data, and other confidential information. Hackers can use this information for nefarious purposes, such as identity theft or financial fraud.
Mobile device security: It is important to properly secure mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Some common security risks include lost or stolen devices leading to unauthorized access to sensitive data, lack of encryption that can make it easier for hackers to intercept data, weak passwords or PINs, unsecured apps that can be compromised by hackers, and outdated software or firmware containing security vulnerabilities.
Information Security 101 for Businesses
Businesses should take proactive steps to mitigate risks and protect their sensitive information. Here are the top 8 easiest-to-implement information security tips for businesses:
-
implemented strong password policies and multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
A strong password should have at least 12 characters and include a mix of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and symbols. It should not contain any personal information such as names, birthdates, or addresses, and should be unique to each account to prevent hackers from accessing multiple accounts with the same password.
Multi-factor authentication, such as requiring a code sent to a mobile device, can also add an extra layer of security to passwords. Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, and Authy are among the most popular multi-factor authentication apps. Available for free on both Android and iOS devices, these apps can add an extra layer of security to online accounts.
-
Regularly update software and security systems.
It is important to regularly update software and security systems to protect against malware and other threats. These updates often include security patches that address known vulnerabilities and help prevent cyber attacks. If software and security systems are not regularly updated, businesses might be left vulnerable to cyber attacks, which can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
-
conduct regular data backups.
Making regular data backups is one of the most important steps businesses can take to ensure the safety and continuity of their operations. Data loss can occur due to a variety of reasons, including system failures, human errors, or cyber attacks. Without proper backups, businesses risk losing valuable data, which can lead to significant disruptions in their operations, lost revenue, and reputational damage. By regularly backing up important data, businesses can ensure that they can quickly and easily recover from a data loss event and resume their normal operations.
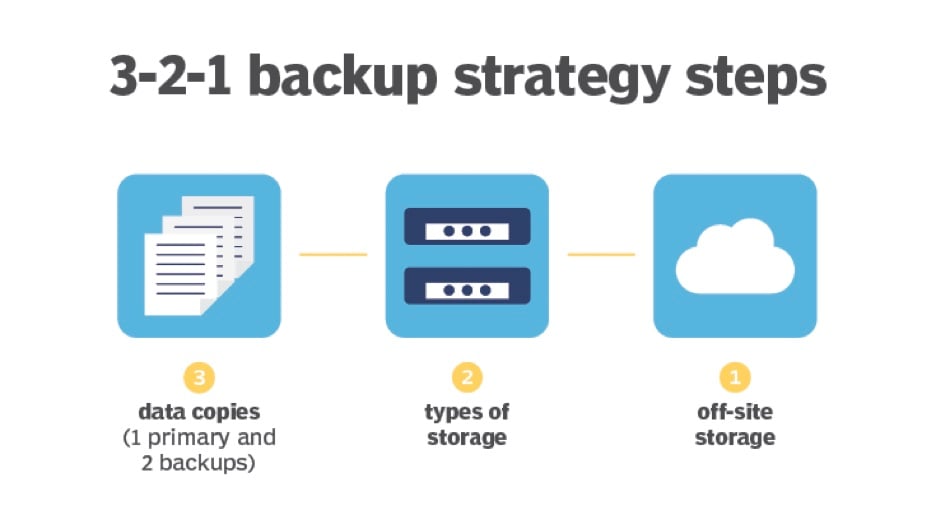
It is recommended to establish a backup schedule that aligns with your business needs and to store backups in locations that are secure and accessible in case of an emergency. It is also important to test backups regularly to ensure that data can be restored quickly and accurately in the event of a data loss. Finally, it is recommended to implement a disaster recovery plan that outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a major data loss, including the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders and the steps to be taken to minimize damage and restore operations as quickly as possible.
-
Train to recognize employees and avoid social engineering attacks such as phishing or pretexting.
Employees can be trained to recognize and avoid social engineering attacks by providing them with regular training sessions that cover the latest threats and tactics used by attackers. These sessions can include simulations of phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics, as well as instructions on how to identify and report suspicious emails or messages. It is critical to emphasize the importance of verifying the authenticity of requests for sensitive information, such as login details or financial data, before responding to them.
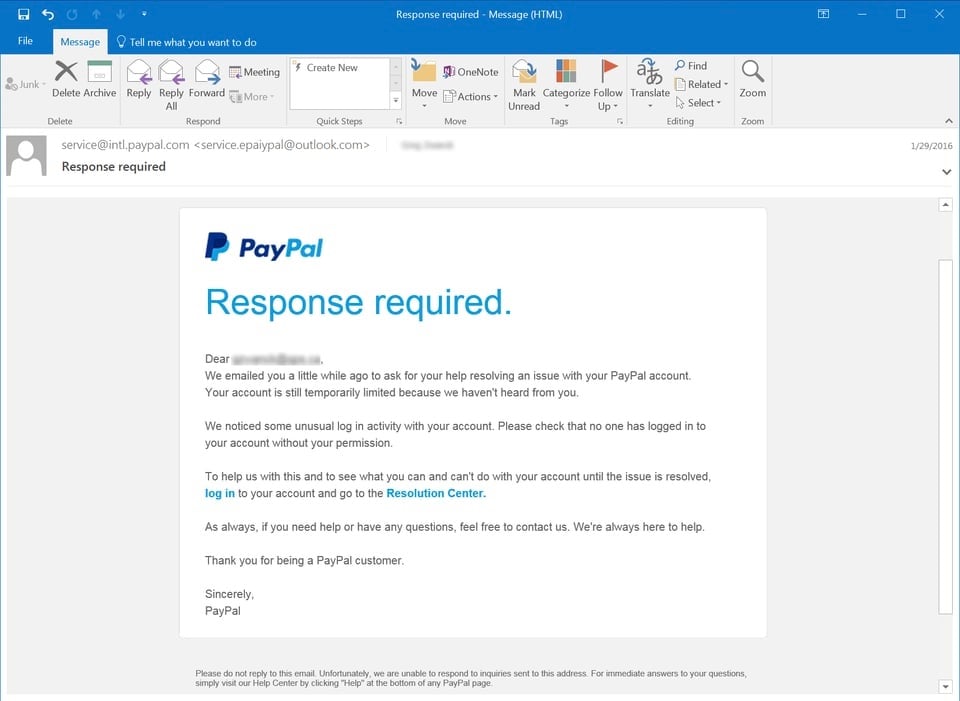
Employees should also be trained to avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources and to report any suspicious activity or requests to their IT department or security team. Finally, as in the case with potential data loss events, it is important to develop and enforce clear security policies and procedures that outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, including the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders and the steps to be taken to minimize damage and restore operations as quickly as possible.
-
implemented security policies for mobile devices to ensure that sensitive data is not stored on these devices.
The most common security policies for mobile devices are essentially the same as for other types of devices. You just need to be aware that mobile devices should also be included in these policies. In addition to implementing password policies, regular software updates, and other previously mentioned tips, mobile devices should also be equipped with remote wipe capabilities to erase data from lost or stolen devices, as well as device tracking or geolocation services to locate lost or stolen devices .
It is important to ensure that all devices used for business purposes, including employee-owned or “bring your own device” (BYOD) devices, are properly secured and that employees are trained to follow established security policies and procedures.
-
Monitor for insider threats and implement appropriate security controls to prevent intentional or accidental breaches of sensitive data.
To identify insider threats, companies can use security measures such as access controls and monitoring software. These measures can prevent intentional or accidental information breaches. By monitoring employee behavior, companies can detect unusual activity that may indicate a security risk.
To protect your company’s data from insider threats, you can use anti-detection multi-accounting browsers. This software enables you to share access to business accounts on various platforms and social media accounts, establish flexible role settings, and track your team members’ detailed profile interaction activity history.
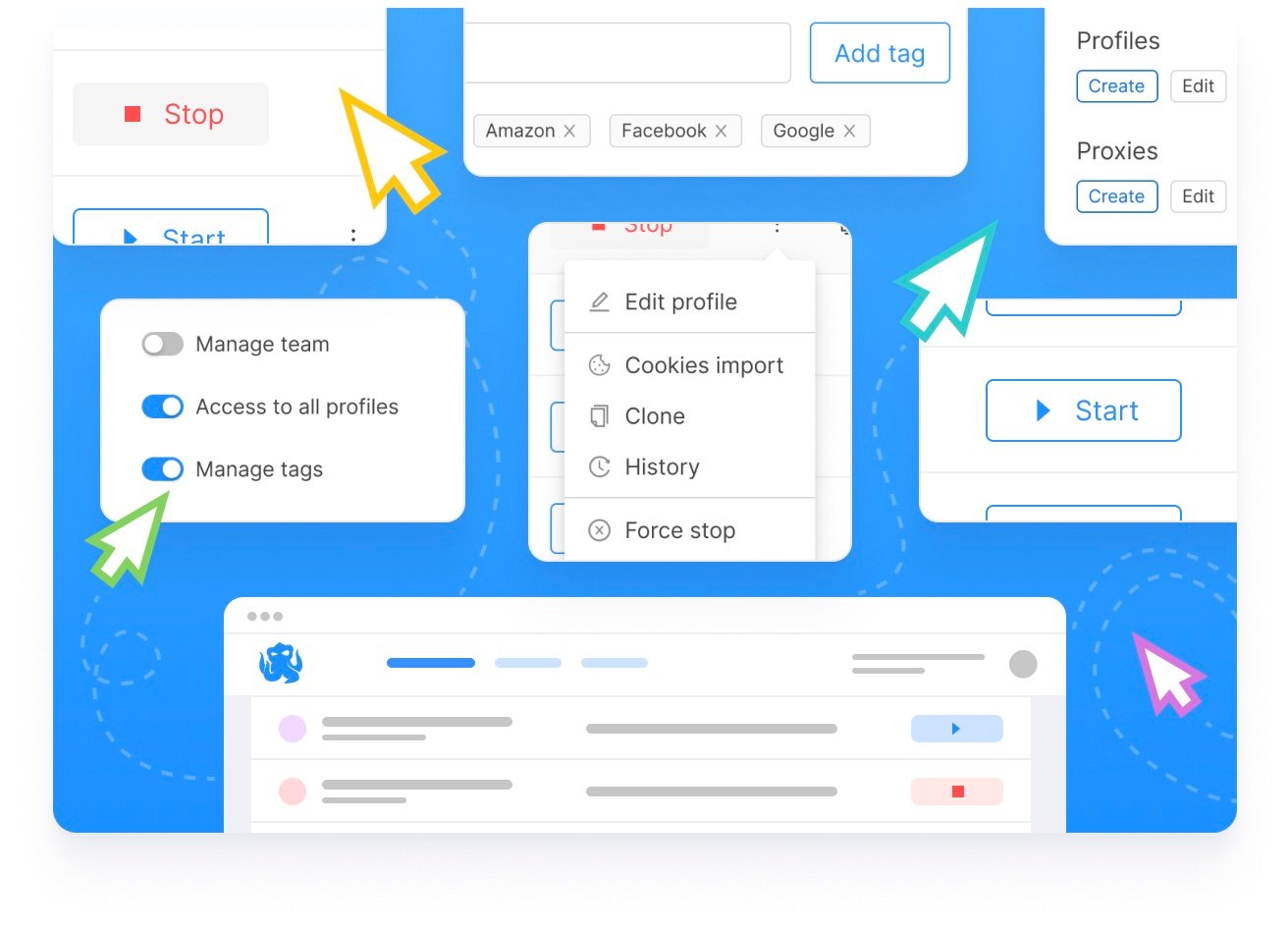
Octo Browser is professional software that allows you to control your profiles in a common workspace using different devices and IP addresses without running into checkpoints or multi-accounting bans. This means, among other things, that your accounts won’t be banned by a platform for running multiple accounts on a limited set of devices. You can also keep track of your employees’ online activities and assign roles to restrict access to sensitive profiles.

-
Conduct due diligence on third-party vendors to ensure that they have adequate security measures in place.
To perform due diligence, you may need to review the security policies and procedures of the vendor, verify their security certifications and compliance with industry standards, and obtain references from other clients or customers.
-
Use encryption to protect sensitive data in transit and at rest.
To protect sensitive data, businesses should use encryption. Encryption involves encoding data so that it can only be read by authorized parties who have the key to decode it. There are two primary types of encryption: symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption.
Symmetric encryption uses a single key to both encrypt and decrypt data. This key must be kept secret to ensure the security of the data. Asymmetric encryption, on the other hand, uses two keys — a public key and a private key — to encrypt and decrypt data. The public key can be shared with anyone, while the private key must be kept secret.
Some common encryption protocols include Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), Transport Layer Security (TLS), and Pretty Good Privacy (PGP).
SSL and TLS are commonly used to encrypt data in transit, such as when sending data over the Internet. To encrypt data with SSL, you will need to have an SSL certificate installed on your server. This certificate will include the public key that is needed to encrypt the data.
PGP, on the other hand, is commonly used to encrypt data at rest, such as when storing data on a hard drive or another storage device. To encrypt data with PGP, you will need PGP encryption software such as Gpg4win or Kleopatra. Once you have installed the software, you can use it to create a PGP key pair, consisting of a public key and a private key. You can share your public key with anyone who needs to send you encrypted messages while keeping your private key safe and secure.
Businesses face a variety of information security risks, including phishing attacks, malware infections, weak passwords, unsecured Wi-Fi networks, and mobile device security threats. Here are the top 8 easiest-to-implement information security tips for businesses:
- Implement strong password policies and multi-factor authentication;
- Regularly update software and security systems;
- Conduct regular data backups;
- Train to recognize employees and avoid social engineering attacks;
- implement security policies for mobile devices;
- Monitor for insider threats;
- conduct due diligence on third-party vendors;
- Use encryption to protect sensitive data in transit.
Useful software to protect businesses includes:
- Multi-factor authentication apps, such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, and Authy;
- Antidetection browsers with teamwork features, such as Octo Browser;
- PGP encryption software, such as Gpg4win or Kleopatra.
Interesting Related Article: “How to Secure Your Brand from Hacking and Fraud”







