A liquidity pool is a smart contract that provides liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEX). It plays a crucial role in the operation of decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols by allowing users to provide liquidity and generate returns. This innovation in the cryptocurrency ecosystem has no equivalent in traditional finance. But how does a liquidity pool actually work and what is its role?
What is a liquidity pool?
To understand how liquidity pools work in decentralized finance (DeFi), it is important to understand how traditional financial markets connect buyers and sellers.
Generally in all types of markets, the buyer offers a purchase price, also called bid price, which represents the maximum amount he is willing to pay for the asset. For his part, the seller offers a selling price, also called ask pricewhich represents the minimum amount he is willing to accept for the asset
In these markets, the Market Makers (market makers) play a vital role in providing liquidity and facilitating trades. Market Makers hold large positions in assets such as stocks, allowing them to quickly match buyers and sellers. Thanks to this liquidity, transactions can be carried out at agreed prices.

However, in the context of decentralized finance-based DEXs, Automated Market Makers (AMM) are used. Prior to the introduction of MAs, liquidity in cryptocurrency markets was a challenge for DEXs on the blockchain Ethereum. At that time, DEXs were a new technology with a complex interface and the number of users was limited, which made it difficult to create a liquid market.
Today, MAs are used in most DEXs. These MAs mainly use mathematical equations to determine prices based on the liquidity available within the pools (we will come back to this). Unlike traditional markets, AMMs do not require order books or intermediary entities to facilitate trading between users. AMMs operate in a decentralized manner and sometimes use oracles, such as those provided by chain linkfor real-time information on cryptocurrency prices.
AMMs solve the problem of limited liquidity by creating pools of liquidity and encouraging users of the protocols to contribute to it by providing liquidity themselves.
The provision of liquidity is implemented through a strategy called liquidity mining, which allows users to earn regular passive income. As a liquidity provider, you are rewarded with a passive return in the protocol’s native cryptocurrency, which encourages you to keep depositing your assets on the platform. This financial incentive aims to encourage the continued participation of liquidity providers and to ensure an adequate level of liquidity on the platform.

The more assets a liquidity pool contains, the easier it is to trade. Liquidity is therefore essential to enable AMMs to match buyers and sellers of assets. Without adequate liquidity, the system is no longer able to function properly.
Trade on the leading DEX


Focus on how Uniswap liquidity pools work
Now that we understand the importance of liquidity pools in decentralized finance, let’s explore how they work, taking the example ofUniswapthe first DEX AMM that appeared in 2018. It is important to note that most of the other DEX AMMs are based on Uniswap, being forked of this protocol.
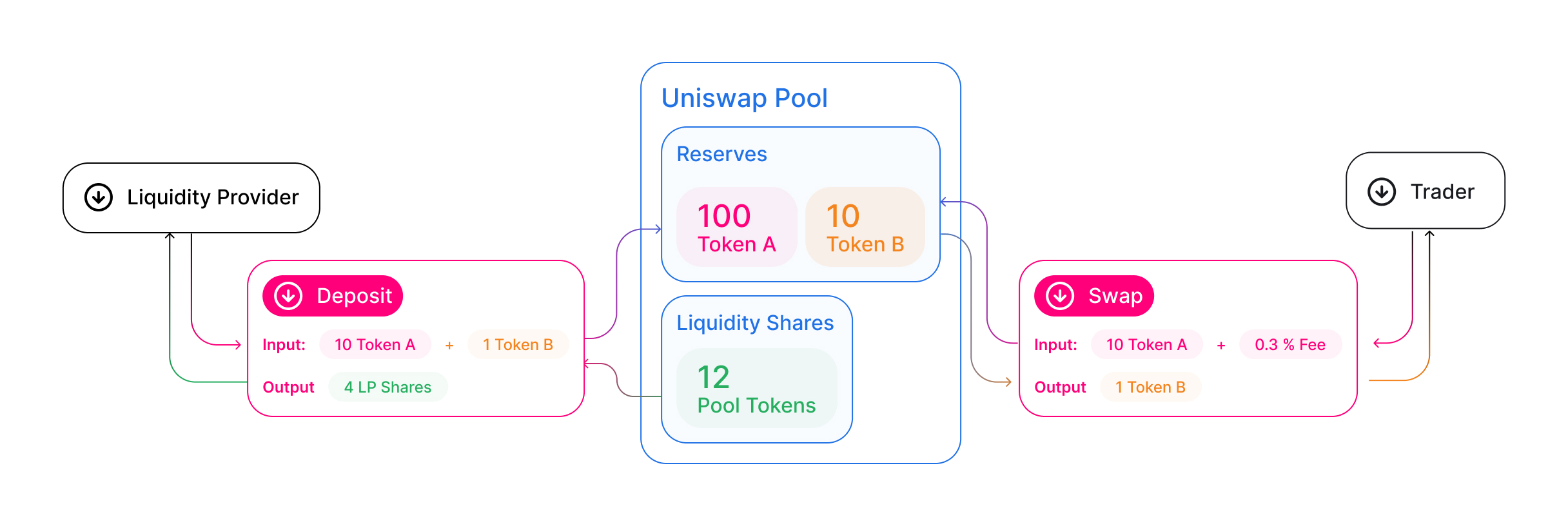
On Uniswap, at the time of creating a liquidity pool, there is no amount of tokens on either side of the pair. In order to enable trading, a user or creator must make an initial deposit of each token. This first liquidity provider thus establishes the initial price of the pool, in addition to being encouraged to deposit a 50/50 ratio of the tokens of the pair.
When a liquidity provider adds funds to a pool, it receives LP tokens (LP for Liquidity Provider) in exchange, representing the share of its contribution to the pool. These LP tokens are tradable assets and can therefore be used freely in the DeFi ecosystem.
Then, liquidity providers are compensated through transaction fees taken from each exchange, usually 0.3%, but sometimes 1% for more “exotic” pairs. These fees are distributed proportionally among all LP token holders, based on their share of participation in the pool. Finally, to recover deposited liquidity as well as accrued fees, liquidity providers must “burn” their LP tokens.

Diagram of how a liquidity pool works on Uniswap
As mentioned above, the AMM determines asset prices using an adjustment algorithm. This algorithm, called constant product algorithm, guarantees that the product of the quantities of the two tokens always remains the same. Thus, a liquidity pool can always provide liquidity, regardless of the size of a transaction, because the algorithm gradually adjusts the price of the token as the desired quantity increases.
Let’s take a concrete example using the ETH/USDC liquidity pool. Suppose there are 2,000,000 USDC tokens and $2,000,000 worth of ETH equals 1,000 ETH, with each ETH worth $2,000.
If a user wants to buy 10 ETH worth $20,000, they will need to provide 20,000 USDC to the pool in exchange for the 10 ETH. After this transaction, the pool is modified. There were 20,000 USDC added and 10 ETH removed from the pool. Nevertheless, the pool always maintains an equal value for each asset. Therefore, the remaining 2,020,000 USDC is considered equivalent to 990 ETH. By taking the ratio of these two quantities, we see that each ETH is now worth $2,040. So, ETH price increased by $40.
Our service dedicated to cryptocurrency investors. Get real-time analytics and optimize your crypto portfolio.

Frequently asked questions about liquidity pools
How much liquidity is in DeFi?
At the time of writing (June 2023), Total Value Locked (TVL) in the DeFi ecosystem is estimated at $47 billion, according to data provided by the DefiLlama site.
Why is having low liquidity a problem?
If a platform lacks liquidity providers, it can lead to high “slippage”, which means the user will get a lower price when trading their cryptocurrencies. Indeed, slippage is the difference between the expected price of a transaction and the price at which the transaction is executed. This is because small token swaps create larger imbalances when the amount of locked tokens in the pool is low. However, high slippage is not the most problematic situation. If a pair does not have sufficient liquidity across all protocols, users will end up with tokens that they cannot sell.
How much does a liquidity provider earn?
The amount of profit generated by a liquidity provider depends on how long it maintains its assets in the liquidity pool. For example, the annual rates of return (APY) of pools on Uniswap typically range between 2% and 10%. To find the optimal return for a particular pool, it is highly recommended to use DEX aggregators such as DefiLlama. These platforms make it possible to compare the returns offered by different pools of liquidity, making it easier to find the best possible return.
Graphic source: Uniswap
Newsletter
Receive a summary of crypto news every Monday by email
What you need to know about affiliate links. This page presents assets, products or services relating to investments. Some links in this article are affiliated. This means that if you buy a product or register on a site from this article, our partner pays us a commission. This allows us to continue to offer you original and useful content. There is no impact on you and you can even get a bonus by using our links.
Investments in cryptocurrencies are risky. Cryptoast is not responsible for the quality of the products or services presented on this page and could not be held responsible, directly or indirectly, for any damage or loss caused following the use of a good or service highlighted in this article. Investments related to crypto-assets are risky by nature, readers should do their own research before taking any action and only invest within the limits of their financial capabilities. This article does not constitute investment advice.
AMF recommendations. There is no guaranteed high return, a product with high return potential involves high risk. This risk-taking must be in line with your project, your investment horizon and your ability to lose part of this savings. Do not invest if you are not ready to lose all or part of your capital.
To go further, read our Financial Situation, Media Transparency and Legal Notices pages.