The Bitcoin blockchain has recently seen a surge in transaction fees with the launch of Babylon, a BTC staking protocol. The latter allows proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchains to benefit from Bitcoin’s security, but raises questions about its implications and risks. Here’s everything you need to know.
What is Babylon, this Bitcoin-based protocol?
In July 2024, the Bitcoin blockchain generated more than $4 million in fees in just 1.5 hours, a record unseen since the last halving, which took place in April 2024 at the time of writing.
This phenomenon is all the more remarkable given the low transaction fees observed between June and August 2024 which reached up to 2 sats/vB, or around $0.20 at that time.

This sudden spike in fees was caused by the launch of a new BTC staking protocol called “Babylon”The latter aims to allow networks operating with a proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism to be secured by the queen of cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin.
When it launched, Babylon set a deposit cap of 1,000 BTC for its users, which is about $60 million at current Bitcoin prices. This limit encouraged investors to rush into the protocol by constantly increasing transaction fees, creating one block in which the average fee exceeded 1,500 sats/vB, or about $200 per transaction.

Babylon logo, styled by Cryptoast
This event has aroused the curiosity of many Internet users, who wondered whether Babylon represented a real opportunity or whether it was simply yet another ephemeral protocol riding on a brief fad.
Download Bitstack and earn €5 in Bitcoin with the code CRYPTOAST5 *
* After activating a savings plan and accumulating at least €100 in BTC purchases
What is staking and restaking?
Bitcoin relies on a proof-of-work (PoW) mechanism in which the rules of the network are protected by a consensus based on computing power, whose main objective is to consume energy to solve an equation, thus representing the production of work.
Since The Merge update on Ethereum, the blockchain uses a Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanismIn this case, the consensus is secured by a quantity of ETH tokens held as a deposit that can be seized in the event of bad behavior by the staker, a process called “slashing”.
To make staking more accessible, protocols like Lido have introduced liquid staking.This mechanism allows users to stake their ETH while receiving in exchange new tokens representing the staked Ethers, called “Liquid Staking Tokens” (LST), or “liquid staked tokens” in French.
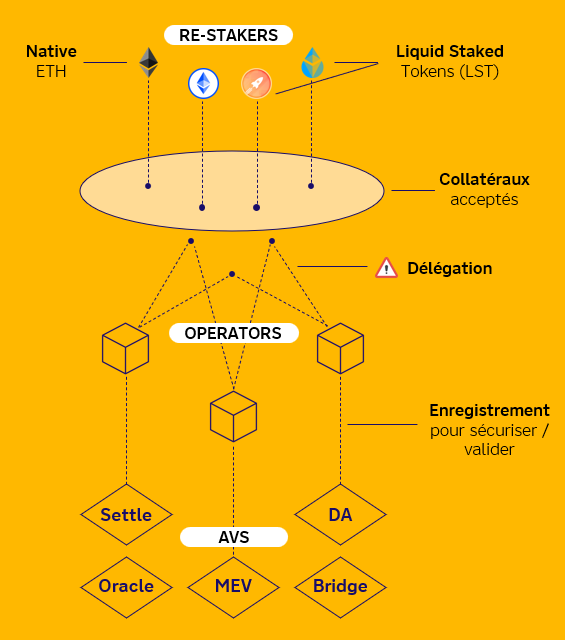
Diagram of roles and actors participating in the retaking of Ethers
This system makes the ETH token more liquid, allowing users to participate in securing the network while granting them some flexibility over how their capital is used.
Retaking, introduced by EigenLayer, goes a step further by allowing validators to lend the economic security of their LST to other systems.beyond the Ethereum blockchain, providing a new layer of protection to these systems.
Swell: the liquid retaking protocol for ETH
Bitcoin's poor programming capabilities are forcing developers to come up with complex solutions to enable the execution of transactions usually made on alternative blockchains.
Built with the Cosmos SDK, the protocol Babylon had to deal with Bitcoin's scripting language, in particular the opcode “OP_CHECKSEQUENCEVERIFY”. This opcode imposes a relative time constraint, called a “timelock”, which notably allowed the creation of the Lightning Network, now allowing Babylon to impose a delay in unlocking staked BTC.
Babylon also uses Extractable One-Time Signatures (EOTS)basic techniques in cryptography that allow anyone to extract a private key if 2 messages are signed with the same key.

This mechanism is designed to ensure security in blockchain validation processes. If a validator signs 2 different blocks at the same height with the same private key, his key is automatically exposed, allowing him to be punished by a slashing mechanism. Thus, EOTS serve to deter malicious behavior.
From the user's perspective, these systems allow sending a transaction on the Bitcoin blockchain to the protocol to lock BTC in a self-custodial secure vault accessible only with the user's private key.
From the perspective of PoS blockchains using Babylon's services, The protocol allows to obtain a finality of transactions guaranteed by the decentralization and immutability of Bitcoin.
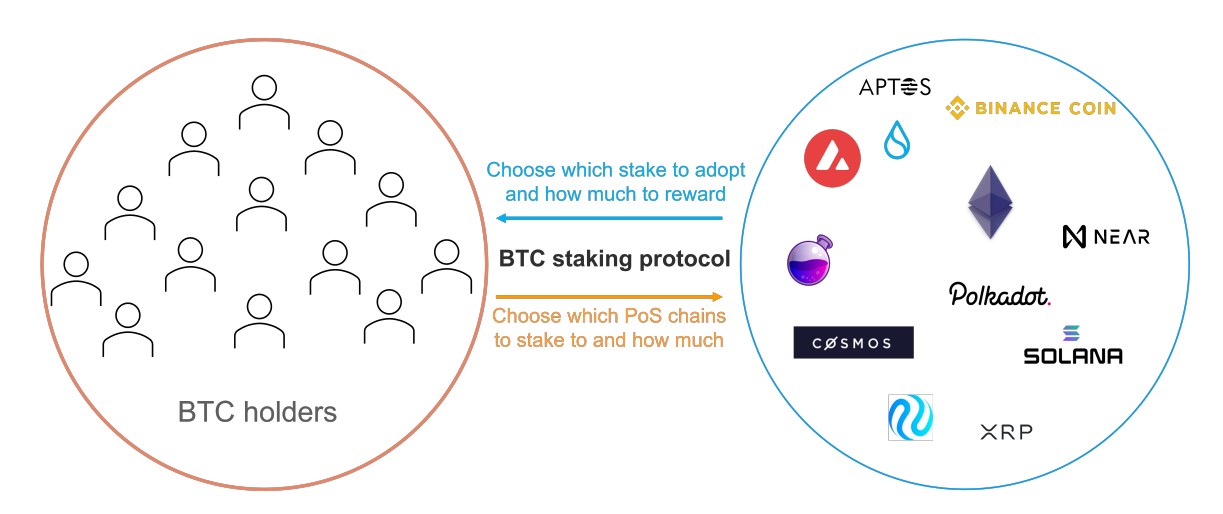
Diagram illustrating the relationship between BTC holders and proof-of-stake based blockchains
In summary, Babylon Protocol aims to create a marketplace where BTC owners and proof-of-stake blockchains can meetBitcoin holders select which networks they want to allocate their tokens to based on the returns on offer, while blockchains determine how much funding they want to offer BTC holders based on the potential security they can gain from it.
So, a few users were able to participate in phase 1 of Babylon and stake 1,000 Bitcoins. In Phase 2, the Babylon blockchain will be launched, allowing the protocol to collect funds and redistribute them. Finally, phase 3, Multi-Staking, will allow BTC to simultaneously secure multiple PoS blockchains, thus generating rewards.
20 € offered when you register on Bitvavo
Babylon's Weaknesses
It is important to note that Babylon's returns are not guaranteed, and so far, stakers only receive points as a reward. Indeed, It is up to the different blockchains operating under PoS to buy the security offered by Babylon, but if none of them find it interesting, the returns will remain zero.
Bitcoin's robustness, decentralization, and censorship resistance are major assets that are likely to attract many users. Although Babylon cannot guarantee the decentralization of a blockchain, which depends primarily on the distribution of its validator nodes, The protocol nevertheless offers greater certainty regarding the immutability of its history and the finality of its transactions..
One of the main risks associated with Babylon is that of BTC centralization, similar to the centralization observed among Bitcoin spot ETF issuers.. While this may not directly affect the sovereignty of the Bitcoin network itself, a malicious actor could exploit this risk in the event of a protocol flaw.

Furthermore, the creation of a reward system based on proof of stake, i.e. the holding of capital, is poorly received by many members of the Bitcoin community, who compare it to the system of government bonds. Such a system is often considered unhealthy, because it rewards the simple holding of assets rather than real work..
Nonetheless, the idea of securing alternative networks with Bitcoin is innovative and worth exploring. In a sense, this represents an improvement on EigenLayer's proposed retaking, which uses Ether as collateral, a more volatile and less proven asset as a store of value compared to Bitcoin..
Cryptoast Research: Don't Spoil This Bull Run, Surround Yourself With Experts
Source: Babylon
The #1 Crypto Newsletter
Receive a daily crypto news recap by email
What you need to know about affiliate links. This page may feature investment-related assets, products, or services. Some links in this article may be affiliate links. This means that if you purchase a product or sign up for a site from this article, our partner pays us a commission. This allows us to continue to provide you with original and useful content. There is no impact on you and you can even get a bonus for using our links.
Investing in cryptocurrencies is risky. Cryptoast is not responsible for the quality of the products or services presented on this page and could not be held responsible, directly or indirectly, for any damage or loss caused following the use of a good or service highlighted in this article. Investments related to crypto-assets are risky by nature, readers must do their own research before taking any action and only invest within the limits of their financial capacities. This article does not constitute investment advice.
AMF recommendations. There is no guaranteed high return, a product with a high return potential implies a high risk. This risk-taking must be in line with your project, your investment horizon and your ability to lose part of these savings. Do not invest if you are not prepared to lose all or part of your capital.
To go further, read our Financial Situation, Media Transparency and Legal Notices pages.










