Current treatments for atrial fibrillation (AFib), a common heart condition characterized by fast and irregular beats that can lead to stroke and heart failure, have multiple side effects and are ineffective for preventing AFib recurrence.
New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and published in Science reveals that certain immune cells play a major role in the development of AFib. Targeting these cells may therefore represent a promising strategy to treat and prevent AFib.
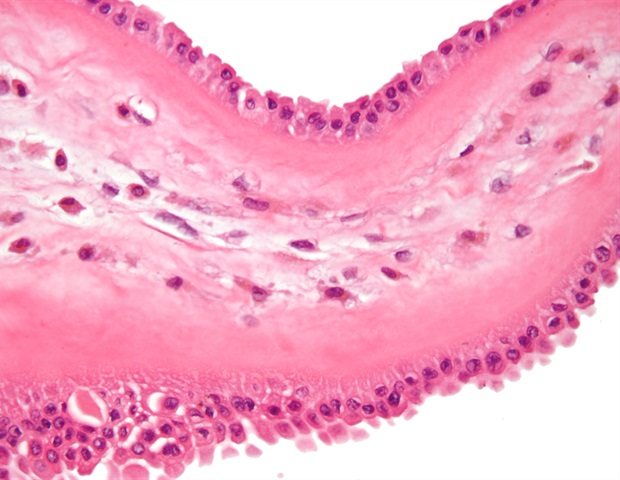
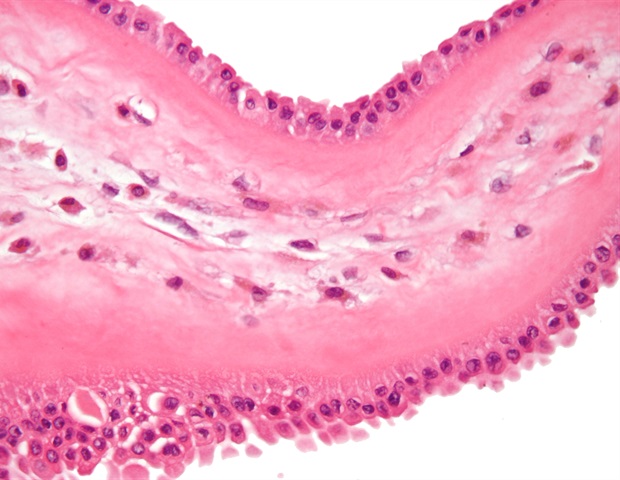
For the work, senior author Matthias Nahrendorf, MD, PhD, an investigator in MGH’s Center for Systems Biology and the Richard Moerschner Endowed MGH Research Institute Chair in Men’s Health, and colleagues analyzed single cells from atrial heart tissue collected from patients with and without AFib. The analyses indicated that immune cells called macrophages are the most dynamic cell population in the atria during AFib, and these cells expand more than any other cell type in diseased tissue.
The researchers also created a new mouse model of AFib they dubbed “HOMER” and tested if and how macrophages can cause AFib.
We found that recruited macrophages support inflammation and fibrosis, or scarring, of the atria, which hinder electrical conduction between heart cells and lead to AFib. Inhibiting macrophage recruitment reduced AFib.”
Matthias Nahrendorf, MD, PhD, Investigator, MGH’s Center for Systems Biology
Gene expression analyses revealed that in human and mouse hearts, the SPP1 gene is highly overexpressed in macrophages during AFib. This gene produces the SPP1 protein (also called osteopontin) that promotes tissue scarring and is elevated in the blood of patients with AFib. HOMER mice lacking this protein had reduced numbers of atrial macrophages.
Future therapeutic strategies for AFib could therefore target macrophages or macrophage-derived signals such as SPP1 that contribute to inflammation and fibrosis. “We think that this research lays the groundwork for immunomodulatory therapy of AFib, and we are currently working on several strategies to make this happen,” says Nahrendorf.
It will also be important to study how these strategies might complement current care. “By mapping cardiac and immune cells involved in atrial fibrillation, this research advances next steps toward studying how macrophage-targeted therapies may support existing treatment,” says Michelle Olive, PhD, the deputy chief of the Atherothrombosis and Coronary Artery Disease Branch within the Division of Cardiovascular Sciences at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Additional co-authors include Maarten Hulsmans, Maximilian J. Schloss, I-Hsiu Lee, Aneesh Bapat, Yoshiko Iwamoto, Claudio Vinegoni, Alexandre Paccalet, Masahiro Yamazoe, Jana Grune, Steffen Pabel, Noor Momin, Hana Seung, Nina Kumowski, Fadi Pulous, Daniel Keller, Constanze Bening, Ursula Green, Jochen K. Lennerz, Richard N. Mitchell, Andrew Lewis, Barbara Casadei, Oriol Iborra-Egea, Antoni Bayes-Genis, Samuel Sossalla, Chin Siang Ong, Richard N. Pierson, Jon C. Aster, David Rohde, Gregory R. Wojtkiewicz, Ralph Weissleder, Filip K. Swirski, George Tellides, George Tolis, Serguei Melnitchouk, David J. Milan, Patrick T. Ellinor, and Kamila Naxerova.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Mercator fellow, DFG, British Heart Foundation, NIHR Oxford Biomedical Research Centre, and European Union MAESTRIA 965286.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) provided partial support for this research, but the release does not represent the official views of NIH.
Source:
Massachusetts General Hospital
Journal reference:
Hulsmans, M., et al. (2023) Recruited macrophages elicit atrial fibrillation. Science doi.org/10.1126/science.abq3061.